 4 Angular Distance - measuring the night sky 4 Angular Distance - measuring the night sky |
 |
If someone asked you to define the word distance, what would you say? If you said something like how far it is from one point to another, then of course you'd be right. For example, the average distance from Earth to Moon is 239,000 miles.
For stargazers, there is a different meaning to the word that is more useful. It is how far one object, like a star, is from another in the dome of our sky. For example, the distance from one end of the Big Dipper to the other is twenty-five degrees, or 25°.
This type of distance is known as angular distance and it is measured in degrees. You probably already know that there are 360° in a circle. This means that the distance from one horizon across the sky to the opposite horizon is 180°, and the distance from the horizon to the zenith, the point directly overhead, is 90°.
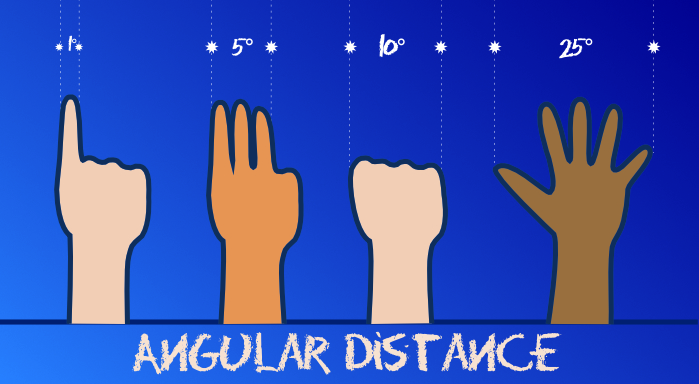
A great way for stargazers to measure angular distance in the sky is to use hands. At arm's length, a single finger width is about 1°, three fingers is 5°, a fist is 10° and an outstretched hand is 25°. (See above). This works for people of all different sizes because, as fingers and hands get bigger, arms tend to get longer too.
Just as hours are divided into minutes and seconds, angular degrees are divided into arcminutes and arcseconds. There are 60 arcminutes in a degree and there are 60 arcseconds in an arcminute.
Some stargazers skip the 'arc' part and just say minutes and seconds -- no problem. Just as the symbol ° is used for degrees, the symbol ' is used for arcminutes and " is used for arcseconds.
How big is an arcminute? Since both the Sun and Moon are 1/2° in diameter and there are 60 arcminutes in a degree, that makes them 30'. Arcminutes are often used to measure the size of DSOs (deep space objects) like clusters and galaxies. The famous Orion Nebula is large at 85' x 60', but the Ring Nebula is small at only 1.4' x 1.1'.
How big is an arcsecond? Since the Moon is 30' and there are 60 arcseconds in an arcminute, that makes it 1,800". Yes, an arcsecond is very small. Arcseconds are used to measure the size of planets in our sky. Jupiter is 50" when it is closest to Earth.
Arcseconds are also used when measuring the separation of stars that are close to each other in our sky. The pairs of double stars in the famous Double-Double in Lyra are 3.5' (arcminutes) apart. But the stars in each pair are a little more than 2" (arcseconds) apart. It takes a sharp telescope, a stable sky and lots of magnification to separate the stars in each pair so you can see them. Can you see all four stars below in our photograph?
Some of the numbers above are good to memorize because degrees, arcminutes and arcseconds are used a lot in stargazing.
|
|
| Finding North ◀️
▶️ Apparent Magnitude |



