| 2024 May 10: Awesome Aurora (2024-5-11) ⬅︎ |
 |
What a spectacular aurora we had on the night of May 10th. So often we see the news about auroras only to be disappointed, but not this time — it was awesome. And we are thrilled that so many people across the country took the time to watch and photograph the event.
Here at Starry Hill, which lies in the shadow of Mt Rainier, we wanted to create a time-lapse video of the aurora above the Mountain. Here is that movie made up of 128 images taken over 10 minutes but sped up to just 32 seconds... about 20 times faster than normal:
As you can see, the aurora at this level was mostly green. Higher up in the sky and outside the view of the video were lots of reds and purples.
What caused the aurora and why all the green and other colors? Here’s the answer in 5 parts:
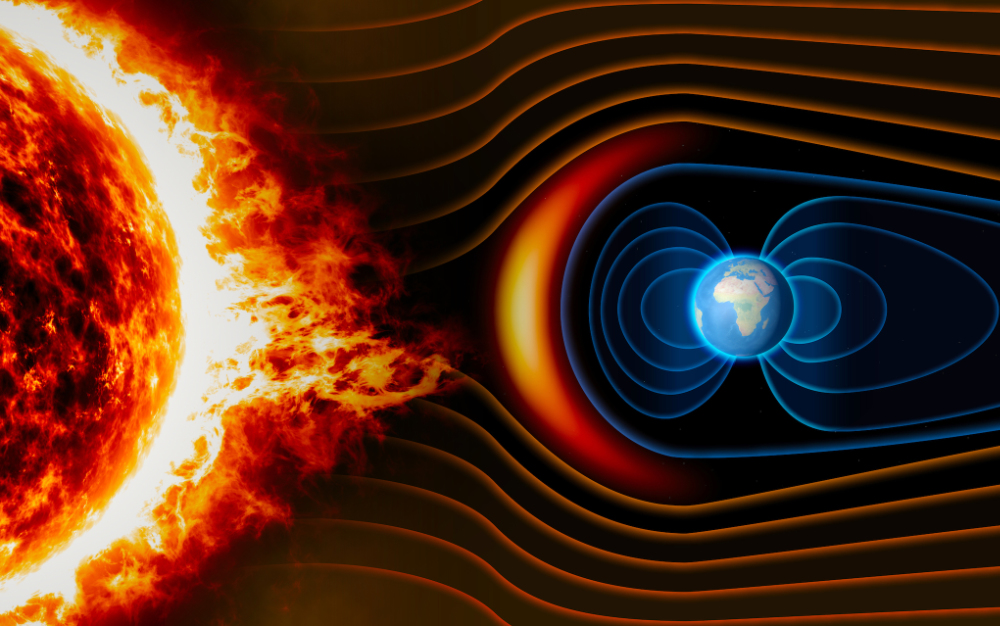
🌟 Solar wind. This is given off by the sun into space at over 1 million mph. Unlike wind on Earth, the solar wind consists of charged particles — protons and electrons. These particles take roughly 2 to 4 days to reach us. You may already be familiar with the solar wind as the cause of tails on comets.
🌟Solar cycle. The sun is magnetically very active. This activity waxes (increases) and wanes (decreases) over an 11 year cycle. When the sun is very active, there is an increase in sunspots and solar flares which can increase the strength of the solar wind potentially doing damage to Earth’s atmosphere, our energy grid and satellites. The peak of the current cycle is expected to be between the years 2023 and 2026 — now!
🌟Geomagnetic field. Fortunately for us, earth has a magnetic field that shields us from the solar wind. It is generated by the motion of liquid iron and nickel deep in Earth’s outer core and extends many thousands of miles into space. Not all planets have magnetic fields to protect them -- when Mars lost its magnetic field, the solar wind stripped away much of its atmosphere.
🌟Aurora. When the solar wind impacts earth, the geomagnetic field acts as a shield by deflecting the particles of the solar wind away from Earth or toward the north and south poles. As these particles descend through Earth’s atmosphere, oxygen and nitrogen gases in our atmosphere become energized and glow — the aurora. The greater the energy, the greater the distance from the poles the aurora can appear.
🌟Colors. Purple and blue mean the charged particles are interacting with nitrogen — the most abundant gas in our atmosphere. Purple occurs with upper-atmosphere nitrogen, and blue with lower-atmosphere nitrogen. Red and green mean the interaction is with oxygen — the 2nd most abundant gas. Red occurs with upper-atmosphere oxygen, and green with lower-atmosphere oxygen.
So cool that, not only is our planet protecting us from the dangerous elements of the Sun, it is showing when and how it is protecting us through a most beautiful display of colorful light that we call the aurora borealis in the northern hemisphere, and the aurora australis in the southern.
For many stargazers, viewing the aurora is a bucket-list item — something that must be experienced at some point in our lives. We hope you got to see this aurora... it was truly awesome!
|
| |



